AI Testcase Designer - Assisted Testcase Authoring using LLMs
Test case development for complex automotive systems is a tedious job because of the vast number of requirements, dependencies, and strict compliance standards that must be satisfied. Manually creating these test cases is time-consuming, error-prone, and often leads to gaps in coverage. In this article, we will see how we can leverage LLM to automate the process.
Introduction
In the automotive domain, software development is tightly governed by standards like ASPICE, where maintaining strict traceability between requirements and acceptance test cases is a core compliance obligation as shown in the below diagram.
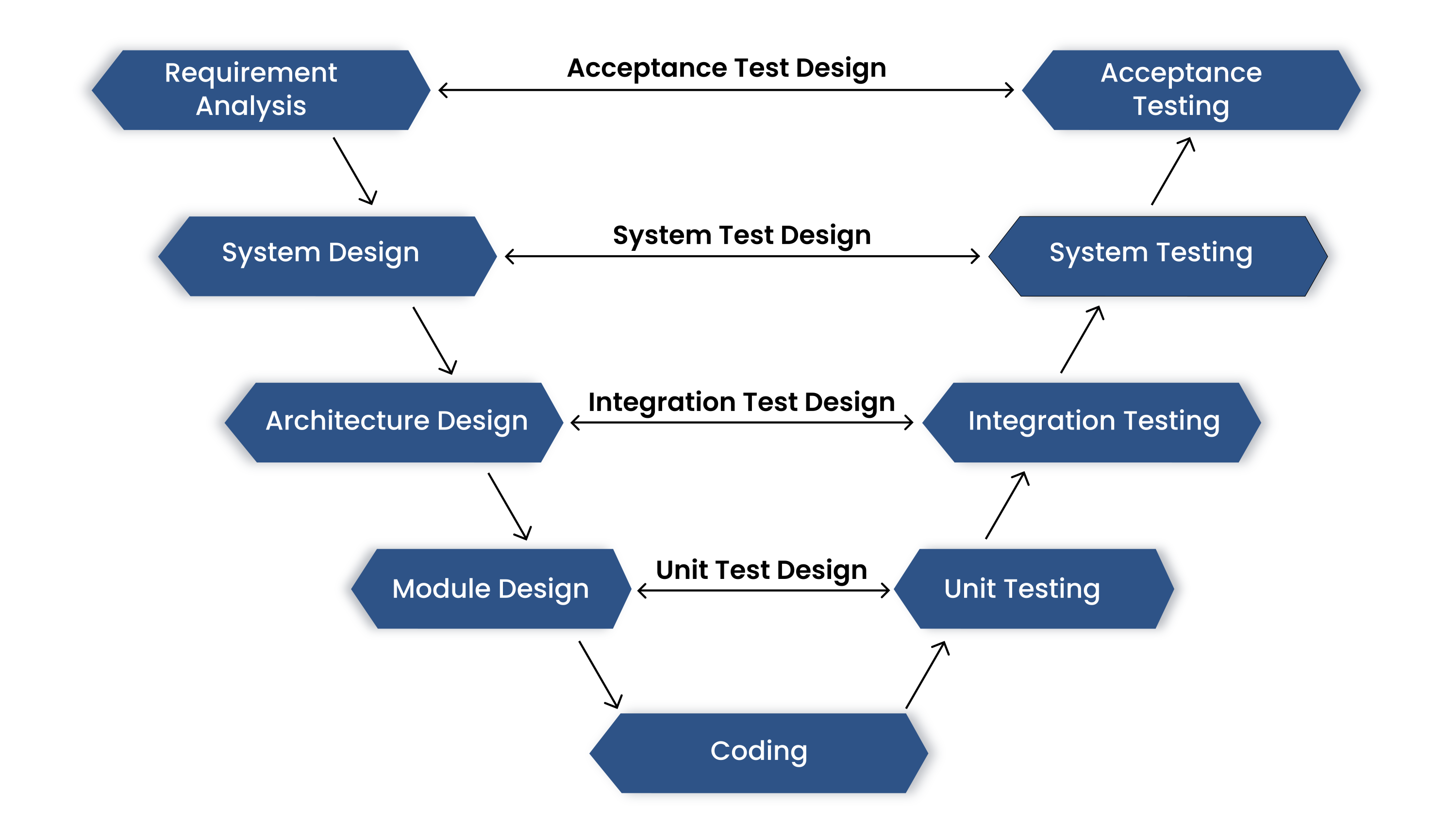
Given the scale and complexity of modern automotive platforms, the number of software and system-level requirements is often substantially large over ~5000 across various ECUs and subsystems. Which are generally created and managed in the ALM(Application Lifecycle Managment) Softwares such as JIRA, Polarion and Codebees.
Problems in Manual Testcase development
Manually developing test cases in projects that have a large amount of requirements and frequent change in requirements creates persistent, systemic problems. Teams routinely face coverage gaps, duplicated effort, and inconsistent test styles across modules or groups. Because requirements evolve—through design updates, optimizations, or bug fixes—test cases must be continuously revised so each change is promptly and correctly validated.
Keeping track of which tests map to which requirements becomes increasingly difficult as the requirement set grows, and manual coordination quickly becomes a maintenance burden. At scale, this slows verification, increases the risk of missed regressions, and undermines compliance in safety‑critical systems.
In short: manual test‑case development struggles with scale, churn, and consistency—posing a significant bottleneck and risk to quality.
Solution: Test Case Generation with LLMs
LLMs can understand natural language requirements and generate structured, consistent test cases automatically.
By leveraging LLMs, we can automate the generation of test cases directly from requirements available in ALMs (like JIRA), and upload the generated test cases with traceable links. Which ensure coverage as the requirements evolve and eliminating manual errors. Thus, providing up-to-date requirements to testcase completion.
LLMs also help ensure full coverage, consistent formatting, and faster updates compared to traditional manual methods.
For testcase generation with LLMs we need these primary components,
-
Model
-
Documents (context)
Choosing a Model
There are multiple model providers and infinite models ranges from running in local machines to Data centers. But, Not all LLMs are created equal. Choosing a best model itself a big task, which is directly proportional to the quality of the generated testcase.
-
Choosing a best model itself a big task, which is directly propotional to the quality of the generated testcase.
To fish out the best model, We use our own LLM Evaluation program. This program compares the each LLM testcase with Golden testcases(Th) through
LLM judge (An state-of-the-art resoning models like GPT-5 or Deepseek) and provide key metrics for test case generation
Those Golden Testcases are manually curated, verified-as-correct testcases that act as the ground truth for comparison
against LLM generated output.
Here are those key metrics,
-
Requirement Understanding: Ability to correctly parse and interpret technical specifications
-
Domain Knowledge: Grasp of automotive terminology and system behaviors
-
Test Coverage: Completeness of generated test scenarios
-
Consistency: Uniformity in test case structure and terminology
-
Performance: Speed and resource usage during generation
For each model, We compare the model generated testcases with Golden testcases using LLM judge :
-
Sample requirements with known test cases
-
Domain-specific terminology checks
-
Complex edge case scenarios
Document: Context for the LLM
Since LLMs don’t inherently know project information, we must feed them structured context:
-
Requirements documents: functional specs, user stories, safety conditions
-
Datasheets and ECU interface definitions
-
Sample test cases or templates, exemplifying your desired syntax and style
-
Domain-specific knowledge, including terminology, signal names, and ECU behaviors
-
Test Setup Description, including hardware configuration, tools and test environment details
Note : If requirements change, you just update the document, the test case designer will automatically generate test cases in click of a button for align to the changes.
Technique Used: Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG)
To optimize both performance and contextual relevance, we adopted Cache‑Augmented Generation (CAG) :
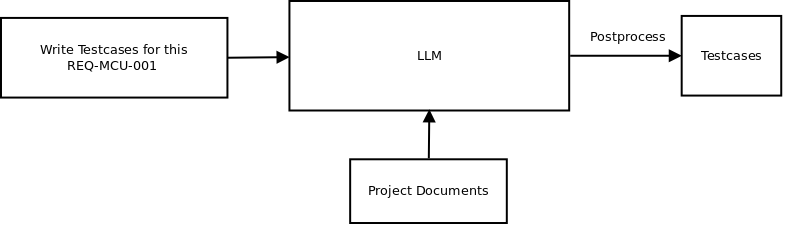
-
Here the project documents such as ALM connection, domain knowledge, datasheets, Test setup description and sample testscases are fed into the LLM’s context.
-
The sample testcases induce a few-shot prompt to generate test cases, without needing to fine-tune.
-
The output then postprocessed to get the structured testcases.
AI Testcase Designer : User Interface
For better usability and demo purpose, We have designed a simple GUI using streamlit.
Testcase Generation
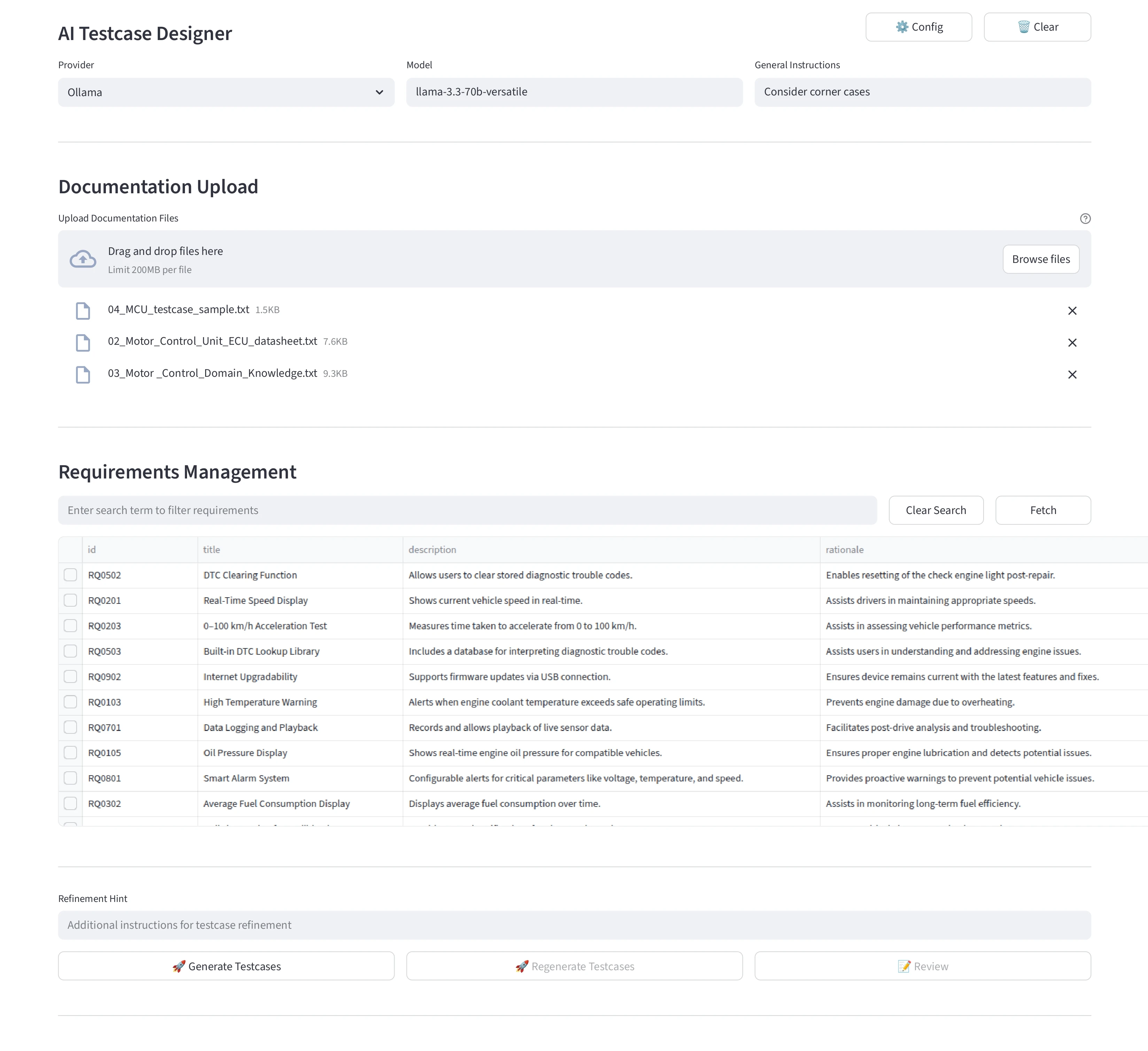
-
Model Selector: Choose the LLM (e.g., Groq, llama-3.3‑70b‑versatile).
-
Config: To configure ALM and LLM Credentials such as URL and tokens.
-
Document Upload: Drag-and-drop datasheets, and sample testcases—these form the model’s context.
-
Fetch: select the requirements to generate testcases.
-
Instruction: Add specific prompts (e.g., consider a specific corner case).
-
Generate Button: Triggers test-case generation.
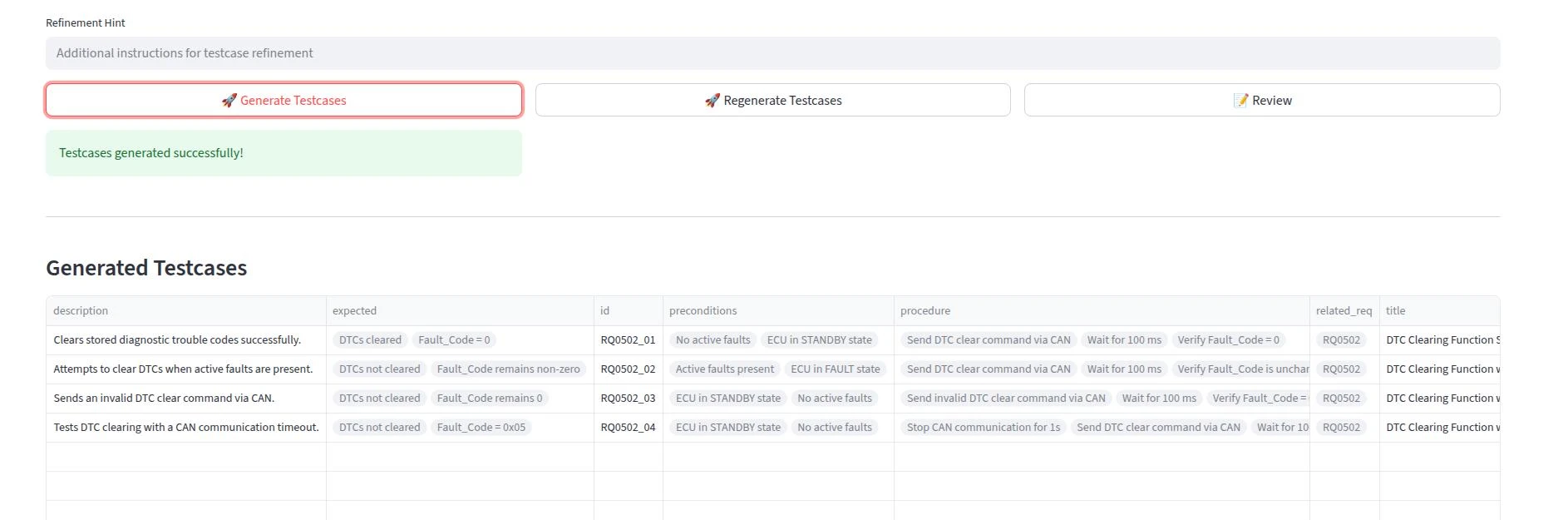
Once the Generate button is triggered, The Test Case Designer will generate testcases for a selected requirements and display them in the Review window.
If test case generation is not satisfactory, the testcases can be regenerated with a Refinement Hint.
-
Preview Panel: Displays structured test cases (ID, title, steps, expected results).
-
Refine Hint (optional): Apply quick adjustments (e.g., “Add edge-case”).
-
Review: To review and update individual testcases.
-
Table Download: To export testcases in Excel format for offline review.
Testcase Review
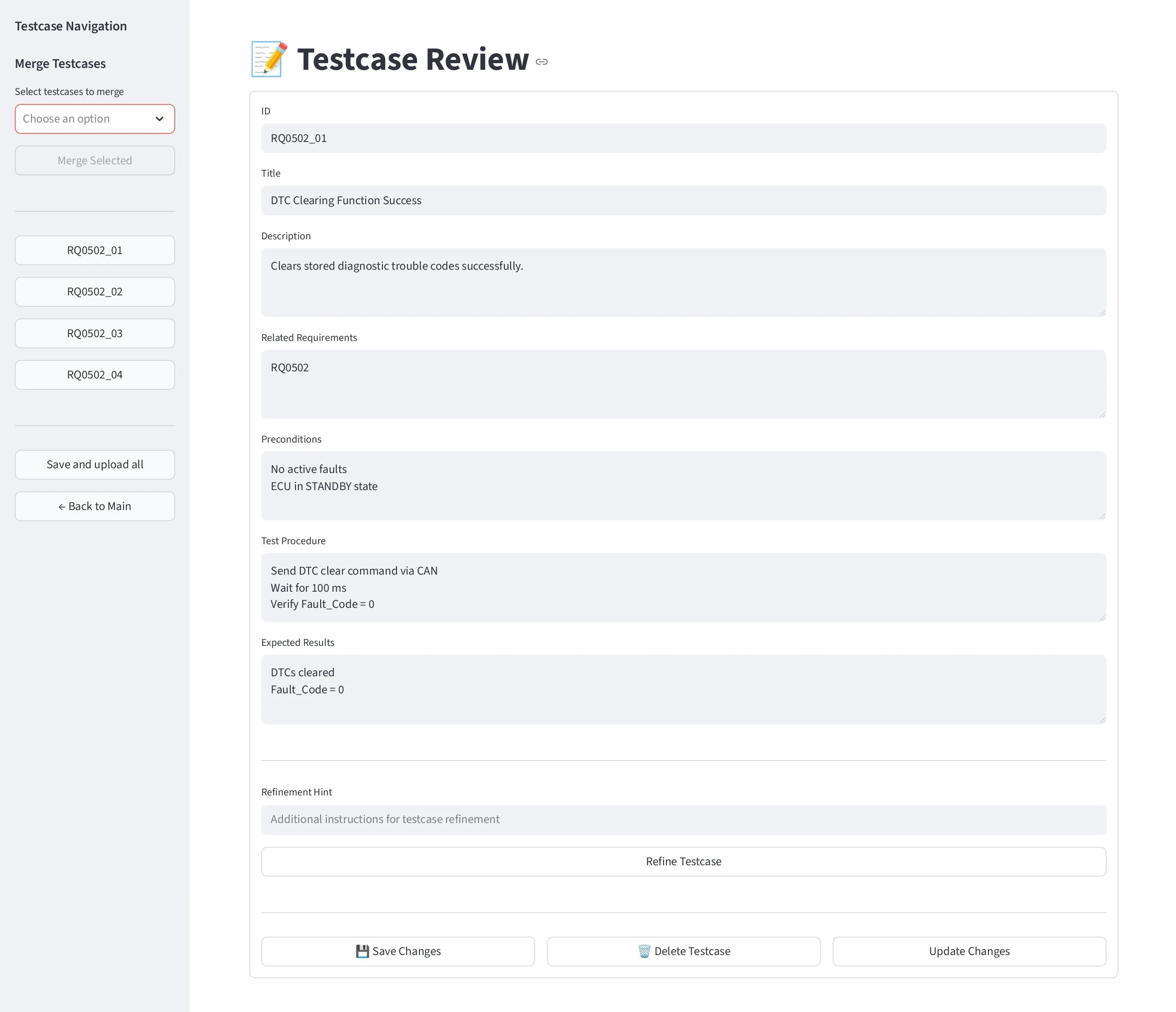
This window enables user to review individual testcases and allow the user to approve or further refine the test case using review comments.
Also, this provides some select options to merge selected testcases into a single testcase without losing its purpose.
-
Once the review is completed, The
Save and upload allbutton can be used to upload all the testcases into configured ALM tool.
Concluding Notes
In summary, the Test Case Designer streamlines the test authoring workflow — fetching requirements from the ALM, generating and refining test cases, and synchronizing them back seamlessly. By leveraging modern LLMs to interpret requirements, user manuals, and test setup descriptions, it significantly reduces the effort of creating and maintaining test cases.
With its intelligent context handling and tight ALM integration, the tool helps teams produce high-quality, traceable test cases at scale. It eliminates manual bottlenecks, keeps QA aligned with evolving requirements, and ensures consistent, compliant outputs — accelerating delivery and enhancing quality. If you are exploring how AI and LLMs can enhance your test case creation and overall QA processes, we would be happy to discuss how our expertise can support you in achieving that.
With our extensive experience working with LLMs and over a decade of deep expertise in building test automation solutions for automotive and embedded systems, we can help design a custom AI tool for test case authoring and reviewing, tailored to your product needs. Reach out to us at sales@zilogic.com to explore further.
References
-
Streamlit - https://streamlit.io
-
Langchan overview - https://python.langchain.com/docs/introduction/
-
Langchan Structured output - https://python.langchain.com/docs/concepts/structured_outputs/
-
Few shot prompt - https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/zero-shot-prompting