Case Study: Elevate WDS Testing with Pitstop
Wireless Distribution System (WDS) is a mechanism that creates 802.11 frames with a 4-address format, and WDS mode is present mainly in Wireless Driver of OpenWRT. WDS mode is required for creating a network connection for larger complex environments that deploy multiple APs with advanced capabilities, which are essential for robust, scalable, and high-performance wireless network connectivity over a wireless link between the access point and the repeater.
Problem
Manually completing these stages can be time-consuming, prone to human error, and frequently involves repetitive tasks. To address these concerns, the Pitstop Framework uses the Robot Framework to automate the WDS feature. This automation streamlines procedures, minimises the possibility of errors, and dramatically increases efficiency.
Implementation
Pitstop is an open-source test automation framework with a wide range of libraries. From single AP setups to complex multi-AP environments, Pitstop streamlines testing processes, enhances test coverage, and provides detailed reporting. This ensures robust performance and reliability in network deployments.
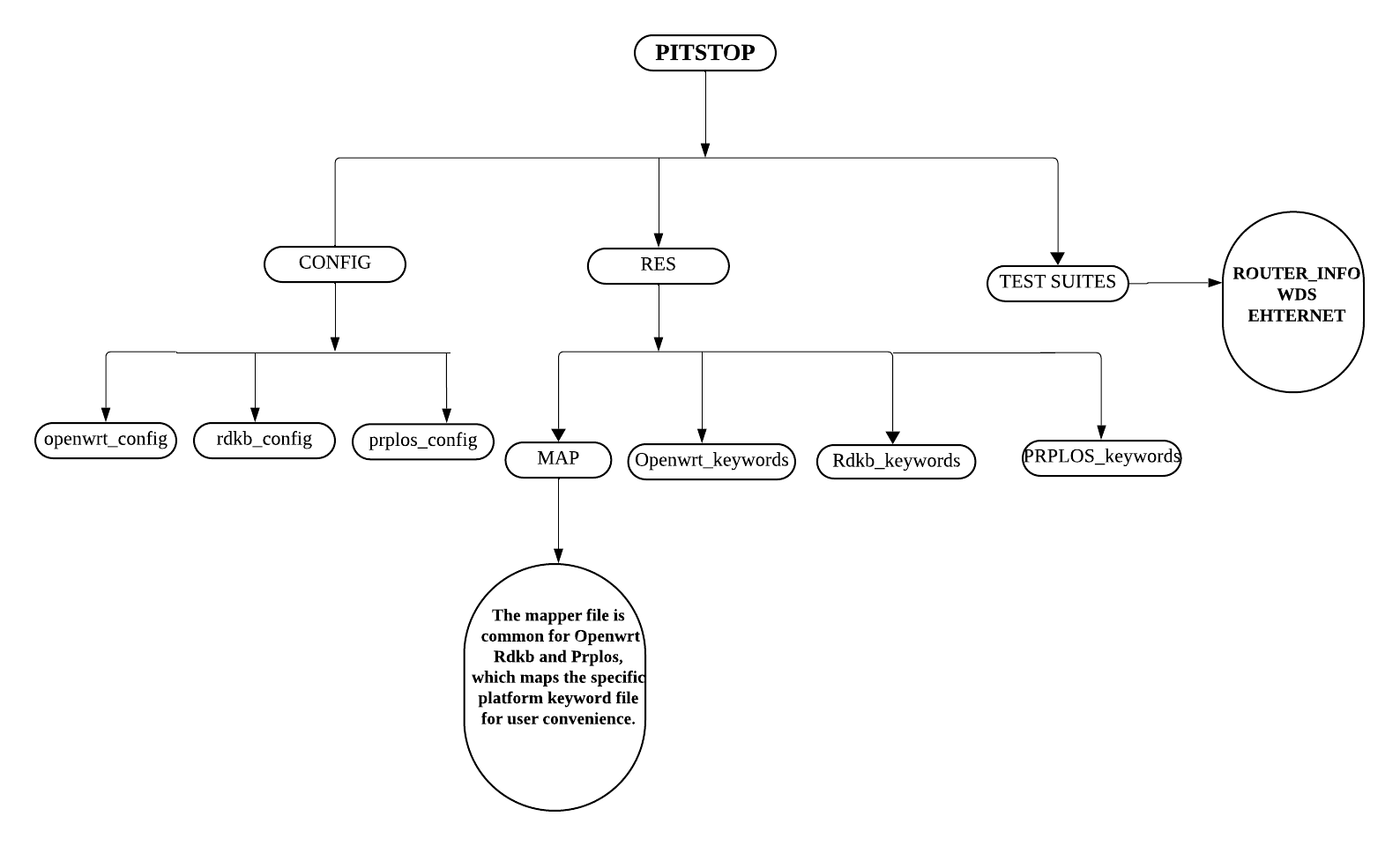
Solution
From a topology perspective, we have the following test bed.
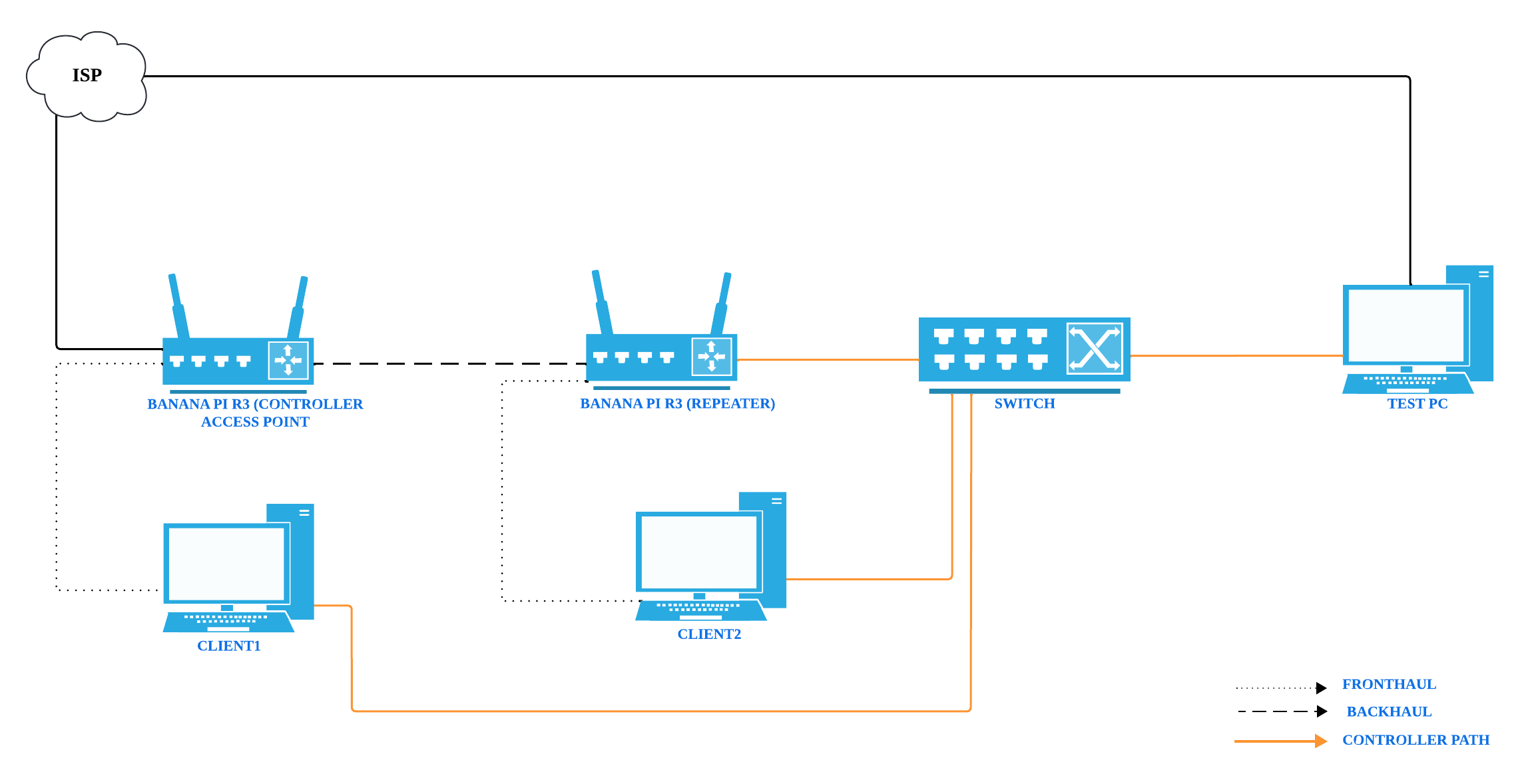
The above setup contains one wireless AP and one wireless repeater. AP is connected to the main network via a wired connection for accessing the internet and repeater acts as an AP client device that creates a direct connection by extending the main network get accessible to both wireless and wired client devices connected to repeater. In this way we can enhance the Wi-Fi coverage in your area.
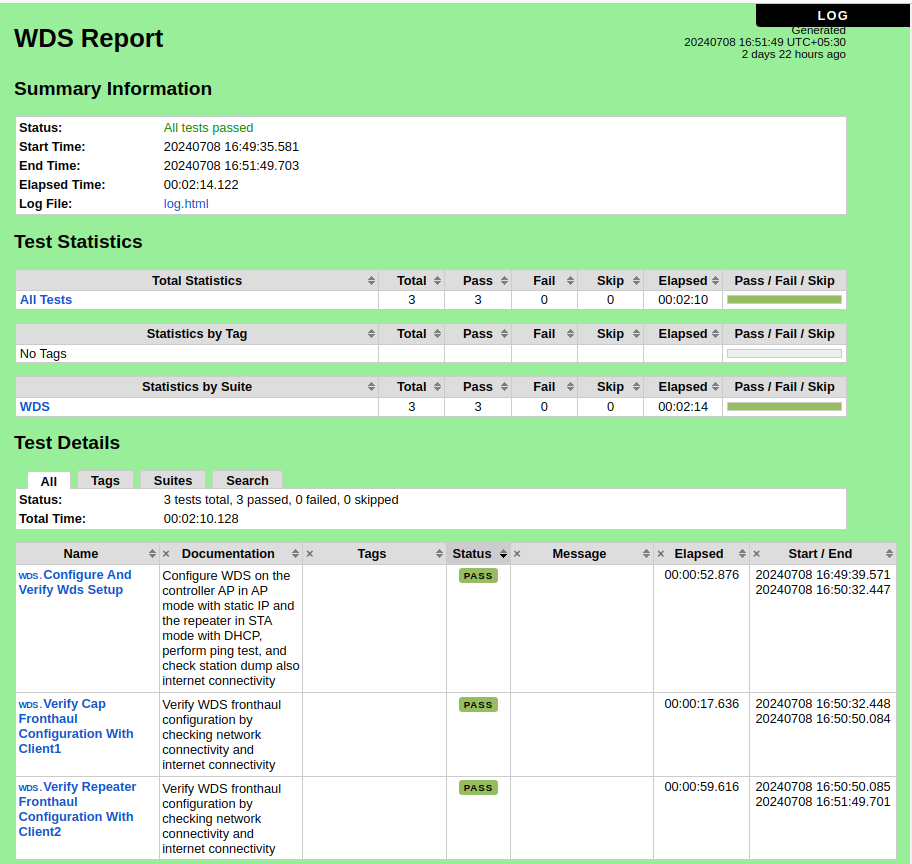
WDS Report
The following figure depicts the test report, which provides an overview of the test results.
Conclusion
By automating the Wireless Distribution System (WDS) feature using the Pitstop Framework and Robot Framework, we have significantly reduced the time and effort required for complex wireless network testing. This solution minimizes human error, accelerates deployment cycles, and improves overall network reliability and performance. This translates into faster time-to-market, reduced operational costs, and enhanced user experience across larger wireless deployments.